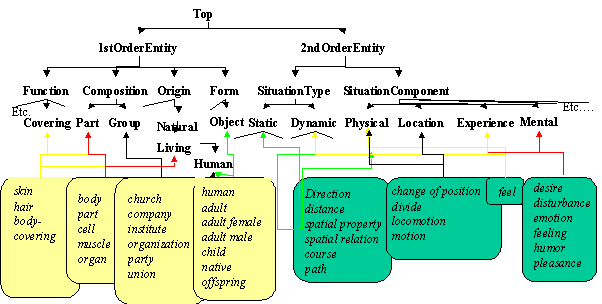
EuroWordNet Top Ontology
The EuroWordNet top-ontology is a lattice structure of 63 features that can be combined in feature combinations (see next Figure). The ontology is specifically designed to help the encoding of the lexical semantic relations in the wordnet in a uniform way. Concrete synsets are classified as 1stOrderEntities that can be specified for 4 Qualia Roles (Pustejovsky 1995): Origin, Form, Composition and Function, e.g.: vehicle is classified as Artifact (Origin) + Object (Form) + Vehicle (Function). Abstract synsets can be 3rdOrderEntities (propositions, ideas, knowledge) or 2ndOrderEntities (events, states, relations). The latter are further classified according to the Aktions-Art class (SituationType: Dunamic or Static)or one or more SituationComponents: Cause, Experience, Mental, Physical, Location, Purpose, Communication, etc. Each 2ndOrder synset has 1 SituationType and a combination of SituationComponents, e.g.: change location is classified as Dynamic + Location + Agentive (Cause) + Physical. A further explanation and motivation of this ontology is given in the EuroWordNet WWW-site.

![]()
1stOrderEntity
*Origin
*Natural *
Living *
Human *
Animal *
Plant *
Creature *
Artifact *
Function
*Building *
Comestible *
Container *
Covering *
Furniture *
Garment *
Instrument *
Occupation *
Place *
Representation *
ImageRepresentation *
LanguageRepresentation *
MoneyRepresentation *
Object *
Substance *
Liquid *
Solid *
Gas *
Composition *
Group *
Part *
![]()
2ndOrderEntity
*SituationType
*Dynamic *
BoundedEvent *
UnboundedEvent *
Static *
Property *
Relation *
SituationComponents *
Cause *
Agentive *
Phenomenal *
Stimulating *
Communication *
Condition *
Existence *
Experience *
Location *
Manner *
Mental *
Modal *
Physical *
Possession *
Purpose *
Quantity *
Social *
Time *
Usage *
![]()
3rdOrderEntity
*1stOrderEntity
|
Any concrete entity (publicly) perceivable by the senses and located at any point in time, in a three-dimensional space. |
Base Concepts
|
Considering the way concrete entities are created or come into existence. |
|
Anything produced by nature and physical forces as opposed to artifact; Opposed to Artifact. |
Base Concepts
{dry land 1; earth 3; ground 7; land 6; solid ground 1; terra firma 1}
{inanimate object 1; object 1; physical object 1}
|
Anything living and dying including objects, organic parts or tissue, bodily fluids; e.g. cells; skin; hair, organism, organs. |
Base Concepts
{being 1; life form 1; living thing 1; organism 1}
{ body 3; organic structure 1; physical structure 1}
|
; e.g. person, someone; Opposed to Plant, Animal, Creature |
Base Concepts
{human 1; individual 1; mortal 1; person 1; someone 1; soul 1}
{worker 2}
|
Imaginary creatures; e.g. god, Faust, E.T.; Opposed to Animal, Human, Plant |
|
; e.g. animal, dog; Opposed to Plant, Human, Creature. |
Base Concepts
{animal 1; animate being 1; beast 1; brute 1; creature 1; fauna 1}
|
; e.g. plant, rice; Opposed to Animal, Human, Creature. |
Base Concepts
{flora 1; plant 1; plant life 1}
|
Anything manufactured by people as natural; Opposed to Natural. |
Base Concepts
{apparel 1; clothes 1; clothing 1; vesture 1; wear 2; wearing apparel 1}
{artefact 1; artifact 1}
{article of furniture 1; furniture 1; piece of furniture 1}
{building 3; edifice 1}
{cloth 1; fabric 1; material 1; textile 1}
{construction 4; structure 1}
{device 2}
{document 2; papers 1; written document 1}
{instrumentality 1; instrumentation 2}
{medium of exchange 1; monetary system 1}
{money 2}
{piece of work 1; work 4}
{product 2; production 2}
{symbol 2}
{writing 4; written material 1}
{written communication 1; written language 1}
|
Considering the purpose, role or main activity of a concrete entity. Typically it can be used for nouns that can refer to any substance, object which is involved in a certain way in some event or process; e.g. remains, product, threat. |
Base Concepts
{asset 2}
{causal agency 1; causal agent 1; cause 1}
{commodity 1; goods 1}
{decoration 2; ornament 1}
{piece of work 1; work 4}
{product 2; production 2}
Base Concepts
{building 3; edifice 1}
Base Concepts
{beverage 1; drink 2; potable 1}
{food 1; nutrient 1}
Base Concepts
Base Concepts
{cloth 1; fabric 1; material 1; textile 1}
Base Concepts
{article of furniture 1; furniture 1; piece of furniture 1}
Base Concepts
{apparel 1; clothes 1; clothing 1; vesture 1; wear 2; wearing apparel 1}
Base Concepts
{device 2}
{instrumentality 1; instrumentation 2}
Base Concepts
{worker 2}
|
Concrete entities functioning as the location for something else; e.g. place, spot, centre, North, South |
Base Concepts
{line 21}
{part 9; region 2}
{place 13; spot 10; topographic point 1}
{point 12}
{dry land 1; earth 3; ground 7; land 6; solid ground 1; terra firma 1}
|
Any concrete entity used for conveying a message; e.g. traffic sign, word, money. |
Base Concepts
{symbol 2}
|
Physical Representations conveyed in a visual medium; e.g. sign language, traffic sign, light signal |
Base Concepts
{line 26}
|
Physical Representations conveyed in language (e.g. spoken, written or sign language); e.g. text, word, utterance, sentence, poem |
Base Concepts
{language unit 1; linguistic unit 1}
{word 1}
{document 2; papers 1; written document 1}
{writing 4; written material 1}
{written communication 1; written language 1}
|
Physical Representations of value, or money; e.g. share, coin |
Base Concepts
{medium of exchange 1; monetary system 1}
{money 2}
FORM
|
Considering the shape of concrete entities, fixed as an object or a-morf as a substance |
|
Any conceptually-countable concrete entity with an outer limit; e.g. book, car, person, brick. Opposed to Substance. |
Base Concepts
{animal 1; animate being 1; beast 1; brute 1; creature 1; fauna 1}
{artefact 1; artifact 1}
{construction 4; structure 1}
{human 1; individual 1; mortal 1; person 1; someone 1; soul 1}
{worker 2}
{inanimate object 1; object 1; physical object 1}
{building 3; edifice 1}
{article of furniture 1; furniture 1; piece of furniture 1}
{device 2}
|
all stuff without boundary or fixed shape, considered from a conceptual point of view not from a linguistic point of view; e.g. mass, material, water, sand, air. Opposed to Object. |
Base Concepts
{chemical compound 1; compound 4}
{chemical element 1; element 6}
{material 5; stuff 7}
{matter 1; substance 1}
{food 1; nutrient 1}
|
Substance that can fall, feels wet and can flow on the ground; e.g. water, soup, rain; Opposed to Gas, Solid. |
Base Concepts
{fluid 2}
{liquid 4}
{beverage 1; drink 2; potable 1}
|
Substance which can fall, does not feel wet and you cannot inhale it; e.g. stone, dust, plastic, ice, metal; Opposed to Liquid, Gas |
Base Concepts
{cloth 1; fabric 1; material 1; textile 1}
{apparel 1; clothes 1; clothing 1; vesture 1; wear 2; wearing apparel 1}
{dry land 1; earth 3; ground 7; land 6; solid ground 1; terra firma 1}
|
Substance that cannot fall, you can inhale it and it floats above the ground; e.g. air, ozon; Opposed to Liquid, Solid. |
|
Considering the composition of concrete entities in terms of parts, groups and larger constructs |
|
Any concrete entity consisting of multiple discrete objects (either homogeneous or heterogeneous sets), typically people, animals, vehicles; e.g. traffic, people, army, herd, fleet |
Base Concepts
{flora 1; plant 1; plant life 1}
{group 1; grouping 1}
|
Any concrete entity which is contained in an object, substance or a group; head, juice, nose, limb, blood, finger, wheel, brick, door |
Base Concepts
{amount 1; measure 1; quantity 1; quantum 1}
{bound 2; boundary 2; bounds 2}
{part 3; portion 2}
{part 12; portion 5}
{dry land 1; earth 3; ground 7; land 6; solid ground 1; terra firma 1}
|
Any Static Situation (property, relation) or Dynamic Situation, which cannot be grasped, heart, seen, felt as an independent physical thing. They can be located in time and occur or take place rather than exist; e.g. continue, occur, apply |
|
Situations implying either a specific transition from one state to another (Bounded in time) or a continuous transition perceived as an ongoing temporally unbounded process; e.g. event, act, action, become, happen, take place, process, habit, change, activity. Opposed to Static. |
Base Concepts
{alter 2; change 12; vary 1}
{change magnitude 1; change size 1}
{change of position 1; motion 2; move 5; movement 2}
{cognition 1; knowledge 1}
{consequence 3; effect 4; outcome 2; result 3; upshot 1}
{decrease 5; diminish 1; fall 11; lessen 1}
{emit 2; express audibly 1; let loose 1; utter 3}
{experience 7; get 18; have 11; receive 8; undergo 2}
{go14; locomote 1; move 15; travel 4}
{locomotion 1; travel 1}
{motion 5; movement 6}
{act together 2; act towards others 1; interact 1}
{act1; human action 1; human activity 1}
{action 1}
{allow 6; let 7; permit 5}
{cover 16}
{convey 1; impart 1}
{evince 1; express 6; show 10}
{express 5; give tongue to 1; utter 1}
{say 8; state 7; tell 7}
|
Dynamic Situations in which a specific transition from one Situation to another is implied; Bounded in time and directed to a result; e.g. to do, to cause to change, to make, to create. |
Base Concepts
{cause 6; get 9; have 7; induce 2; make 12; stimulate 3}
{cause 7; do 5; give rise to 1; make 17}
{cease 3; discontinue 2; give up 12; lay off 2; quit 5; stop 20}
{change 1}
{change of location 1; motion 1; move 4; movement 1}
{create 2; make 13}
{furnish 1; provide 3; render 12; supply 6}
{get hold of 2; take 17}
{happening 1; natural event 1; occurrence 1}
{kill 5}
{remove 2; take 4; take away 1}
{cerebrate 1; cogitate 1; think 4}
{give 16}
|
Dynamic Situations occurring during a period of time and composed of a sequence of (micro-)changes of state, which are not perceived as relevant for characterizing the Situation as a whole; e.g. grow, continuous changing, move around, live, breath, activity, hobby, sport, education, work, performance, fight, love, caring, management. |
Base Concepts
{communicate 1; intercommunicate 1; transmit feelings 1; transmit thoughts 1}
{remember 2; think of 1}
{time 1}
{consume 2; have 8; ingest 2; take 16}
|
Situations (properties, relations and states) in which there is no transition from one eventuality or situation to another: non-dynamic; e.g. state, property, be. Opposed to Dynamic. |
Base Concepts
{ be 4; have the quality of being 1}
{state 1}
{unit 6; unit of measurement 1}
|
Static Situation which applies to a single concrete entity or abstract Situation; e.g. colour, speed, age, length, size, shape, weight. |
Base Concepts
{character 2; lineament 2; quality 4}
{attribute 2; dimension 3; property 3}
{condition 5; status 2}
{need 5; require 3; want 5}
{need 6}
{situation 4; state of affairs 1}
{ability 2; power 3}
{color 2; coloring 2; colour 2; colouring 2}
{form 1; shape 1}
{form 6; pattern 5; shape 5}
|
Static Situation which applies to a pair of concrete entities or abstract Situations, and which cannot exist by itself without either one of the involved entities; e.g. relation, kinship, distance, space. |
Base Concepts
{be 9; occupy a certain area 1; occupy a certain position 1}
{direction 7; way 8}
{space 1}
{spacing 1; spatial arrangement 1}
{have 12; have got 1; hold 19}
{aim 4; bearing 5; heading 2}
{course 7; trend 3}
{path 3; route 2}
{spatial property 1; spatiality 1}
{ratio 1}
|
Situations involving causation of Situations (both Static and Dynamic); result, effect, cause, prevent. |
|
|
|
Causation is always combined with Dynamic and it can take various forms. It can either be related to a controlling agent which intentionally tries to achieve some change (Agentive), or it can be related to some natural force or circumstance (Phenomenal). Another differentiation is into the kind of effect as a perceptive or mental Experience, which makes the cause Stimulating. The different ways of causation have been subdivided in terms of an extra level of TCs. |
Base Concepts
{act 1;human action 1; human activity 1}
{action 1}
{allow 6; let 7; permit 5}
{cover 16}
{cause 6; get 9; have 7; induce 2; make 12; stimulate 3}
{cause 7; do 5; give rise to 1; make 17}
{cease 3; discontinue 2; give up 12; lay off 2; quit 5; stop 20}
{change 1}
{create 2; make 13}
{furnish 1; provide 3; render 12; supply 6}
{kill 5}
|
Situations in which a controlling agent causes a dynamic change; e.g. to kill, to do; to act. Opposed to other causes such as Stimuli, Forces, Chance, Phenomena. |
Base Concepts
{act together 2; act towards others 1; interact 1}
{cerebrate 1; cogitate 1; think 4}
{communicate 1; intercommunicate 1; transmit feelings 1; transmit thoughts 1}
{convey 1; impart 1}
{evince 1; express 6; show 10}
{express 5; give tongue to 1; utter 1}
{give 16}
{remember 2; think of 1}
{say 8; state 7; tell 7}
|
Situations that occur in nature controlled or uncontrolled or considered as a force; e.g. weather, chance. Opposed to other causes such as Stimuli, Agents. |
Base Concepts
{consequence 3; effect 4; outcome 2; result 3; upshot 1}
|
Situations in which something elicits or arouses a perception or provides the motivation for some event, e.g. sounds (song, bang, beep, rattle, snore), views, smells, appetizing, motivation. Opposed to other causes such as Agents, Forces, Chance. |
Base Concepts
{emit 2; express audibly 1; let loose 1; utter 3}
{color 2; coloring 2; colour 2; colouring 2}
{form 6; pattern 5; shape 5}
|
Situations involving communication, either Static, e.g. be_about or Dynamic (Bounded and Unbounded); e.g. speak, tell, listen, command, order, ask, state, statement, conversation, call. |
|
Communication verbs and nouns are often speech-acts (bounded events) or denote more global communicative activities (unbounded events) but there are also a few Static Communication BCs. The Static Communication BCs (e.g. to be about) express meaning relations between PhysicalRepresentations (such as written language) and the propositional content (3rdOrderEntities). The Dynamic BCs below the TC Communication form a complex cluster of related concepts. They can represent various aspects of Communication which correlate with the different ways in which the communication is brought about, or different phases of the communication. Some Communication BCs refer to causation of communication effects, such as to explain, to show, to demonstrate, but not necessarily to the precise medium (graphical, verbal, body expression). These BCs combine with the TCs Cause and Mental. Other BCs refer to the creation of a meaningful Representation, to write, to draw, to say, but they do not necessarily imply a communicative effect or the perception and interpretation of the Representation. They typically combine with Existence, Agentive, and Purpose. Yet other BCs refer to the perceptual and mental processing of communicative events, to read, to listen and thus combine with Mental. |
Base Concepts
{communicate 1; intercommunicate 1; transmit feelings 1; transmit thoughts 1}
{convey 1; impart 1}
{evince 1; express 6; show 10}
{express 5; give tongue to 1; utter 1}
{say 8; state 7; tell 7}
|
Situations involving an evaluative state of something: Static, e.g. health, disease, success or Dynamic e.g. worsen, improve. |
|
|
|
Condition is an evaluative notion that can be either positive or negative. It can be combined with Dynamic changes (Social, Physical or Mental) or Static Situations which are considered as positive or negative (again Social, Physical or Mental). |
Base Concepts
{condition 5; status 2}
{need 5; require 3; want 5}
{need 6}
{situation 4; state of affairs 1}
{cause 7; do 5; give rise to 1; make 17}
|
Situations involving the existence of objects and substances; Static states of existence e.g. exist, be, be alive, life, live, death; Dynamic changes in existence; e.g. kill, produce, make, create, destroy, die, birth. |
|
|
|
Dynamic Existence Situations typically refer to the coming about, the dying or destruction of both natural and artifact entities. This includes artificial production or creation, such as to make, to produce, to create, to invent, and natural birth. Static Existence is a small cluster of nouns that refer to existence or non-existence. |
Base Concepts
{create 2; make 13}
{kill 5}
|
Situations that involve an experiencer: either mental or perceptual through the senses. |
|
|
|
Situations with the TC Experience involve the mental or perceptual processing of some stimulus. In this respect there must be an experiencer implied, although it is not necessarily expressed as one of the arguments of a verb (it could be incorporated in the meaning). Typical Experience BCs are: to experience, to sense, to feel, pain, to notice. Experiences can be differentiated by combining it with Physical or Mental. Physical Experiences are external stimuli processed by the senses: to see, to hear. Mental Experiences are internal only existing in our minds: desire, pleasance, humor, faith, motivation. There are many examples of BCs that cannot be differentiated between these, e.g. pain that can be both Physical and Mental. Another interesting aspect of Experiences is that there is unclarity about the dynamicity. It is not clear whether a feeling or emotion is static or dynamic. In this respect Experience BCs are often classified as SituationType, which is undifferentiated for dynamicity. |
Base Concepts
{cognition 1; knowledge 1}
{experience 7; get 18; have 11; receive 8; undergo 2}
|
Situations involving spatial relations; static e.g. level, distance, separation, course, track, way, path; something changes location, irrespective of the causation of the change; e.g. move, put, fall, drop, drag, glide, fill, pour, empty, take out, enter. |
|
Location is typically incorporated in Dynamic BCs denoting movements. When combined with Static it clusters nouns that refer to Location Relations, such as distance, level, path, space. A Location Relation holds between several entities and cannot be seen as a property of single entity. This makes it different from Place, which applies to a 1stOrderEntity that functions as the location for an event or some other 1stOrderEntity. |
Base Concepts
{ aim4; bearing 5; heading 2}
{be 9; occupy a certain area 1; occupy a certain position 1}
{consume 2; have 8; ingest 2; take 16}
{course 7; trend 3}
{direction 7; way 8}
{path 3; route 2}
{space 1}
{spacing 1; spatial arrangement 1}
{spatial property 1; spatiality 1}
{change of location 1; motion 1; move 4; movement 1}
{get hold of 2; take 17}
{remove 2; take 4; take away 1}
{change of position 1; motion 2; move 5; movement 2}
{go 14; locomote 1; move 15; travel 4}
{locomotion 1; travel 1}
{motion 5; movement 6}
{furnish 1; provide 3; render 12; supply 6}
|
Situations in which way or manner plays a role. This may be Manner incorporated in a dynamic situation, e.g. ways of movement such as walk, swim, fly, or the static Property itself: e.g. manner, sloppy, strongly, way. |
|
|
|
Manner as a SituationComponent applies to many specific BCs that denote a specific way or manner in which a Dynamic event takes place. Typical examples are ways of movement. General BCs that only refer to Manner as such and not to some specific Situation are Static nouns such as manner, way, style. |
Base Concepts
|
Situations experienced in mind, including a concept, idea or the interpretation or message conveyed by a symbol or performance (meaning, denotation, content, topic, story, message, interpretation) and emotional and attitudinal situations; a mental state is changed; e.g. invent, remember, learn, think, consider. Opposed to Physical. |
|
|
|
Mental Situations can be differentiated into Experiences (see Experience) and in Dynamic Mental events possibly involving an Agent. The latter cluster cognitive actions and activities such as to think, to calculate, to remember, to decide. |
Base Concepts
{remember 2; think of 1}
{cerebrate 1; cogitate 1; think 4}
{cognition 1; knowledge 1}
{ability 2; power 3}
|
Situations (only Static) involving the possibility or likelihood of other situations as actual situations; e.g. abilities, power, force, strength. |
|
|
|
Modal Situations are always Static. Most Modal BCs denote some ability or necessary property needed to perform some act or activity. |
Base Concepts
|
Situations involving perceptual and measurable properties of first order entities; either Static e.g. health, a colour, a shape, a smell; or Dynamic changes and perceptions of the physical properties of first order entities; e.g. redden, thicken, widen, enlarge, crush, form, shape, fold, wrap, thicken, to see, hear, notice, smell. Opposed to Mental. |
|
Physical typically clusters Dynamic physical Changes, in which a Physical Property is altered, and Static Physical Properties. In all these cases a particular physical property is incorporated which, in many cases, can be made explicit by means of a causative relation (to become red) or a synonymy relation (health and healthy) with an adjective in the local wordnets. Another cluster is formed by Physical Experiences (see Experience). |
Base Concepts
{color 2; coloring 2; colour 2; colouring 2}
{form 1; shape 1}
{form 6; pattern 5; shape 5}
{ratio 1}
{emit 2; express audibly 1; let loose 1; utter 3}
{aim 4;bearing 5; heading 2}
{consume 2; have 8; ingest 2; take 16}
{course 7; trend 3}
{path 3; route 2}
{spatial property 1; spatiality 1}
{cover 16}
{change of location 1; motion 1; move 4; movement 1}
{get hold of 2; take 17}
{remove 2; take 4; take away 1}
{change of position 1; motion 2; move 5; movement 2}
{locomotion 1; travel 1}
{motion 5; movement 6}
{create 2; make 13}
{kill 5}
{furnish 1; provide 3; render 12; supply 6}
|
Situations involving possession; Static e.g. have, possess, possession, contain, consist of, own; Dynamic changes in possession, often to be combined which changes in location as well; e.g. sell, buy, give, donate, steal, take, receive, send. |
|
|
|
Possession covers ownership and changes of ownership, but not physical location or meronymy or abstract possession of properties. The fact that transfer of Possession often implies physical motion or static location will be indicated by cross-classifying BCs for Possession, Location, and Static or Dynamic, respectively. |
Base Concepts
{have 12; have got 1; hold 19}
{give 16}
{get hold of 2; take 17}
{furnish 1; provide 3; render 12; supply 6}
|
Situations which are intended to have some effect. |
|
|
|
Purpose is an abstract component reflecting the intentionality of acts and activities. This concept can only be applied to Dynamic Situations and it strongly correlates with Agentive and Cause, clustering mainly human acts and activities. SituationComponents such as Usage, Social and Communication often (but not always) combine with Purpose. |
Base Concepts
{unit 6; unit of measurement 1}
{consume 2; have 8; ingest 2; take 16}
{cerebrate 1; cogitate 1; think 4}
|
Situations involving quantity and measure; Static e.g. weight, heaviness, lightness; changes of the quantity of first order entities; Dynamic e.g. to lessen, increase, decrease. Dynamic BCs clustered below Quantity typically denote increase or decrease of amounts of entities. Static Quantity BCs denote all kinds of measurements. |
Base Concepts
{amount of time 1; period 3; period of time 1; time period 1}
{change magnitude 1; change size 1}
{decrease 5; diminish 1; fall 11; lessen 1}
{ratio 1}
{unit 6; unit of measurement 1}
|
Situations related to society and social interaction of people: Static e.g. employment, poor, rich, Dynamic e.g. work, management, recreation, religion, science. |
|
|
|
Social refers to our inter-human activities and situations in society. There are many Social activities (UnboundedEvent) which correlate with many different Social Interests or Purposes. These are not further differentiated in terms of TCs but using the Domain labels (Management, Science, Religion, Health Care, War, Recreation, Sports). In addition there are Static Social states such as poverty, employment. |
Base Concepts
{act together 2; act towards others 1; interact 1}
{unit 6; unit of measurement 1}
|
Situations in which duration or time plays a significant role; Static yesterday, day, pass, long, period, Dynamic e.g. begin, end, last, continue. |
|
|
|
Time is only applied to BCs that strongly imply temporal aspects. This includes general BCs that only imply some temporal aspect and specific BCs that also denote some specific Situation. Typical 'aspectual' BCs, such as begin, end, only express to the phase of situations but abstract from the actual Situation. Most of these also imply dynamicity. More specific BCs, such as to attack, to depart, to arrive, combine other SituationComponents but also imply some phase. Finally, all BCs that denote time points and periods, such as time, day, hour, moment, are all clustered below Time and Static. |
Base Concepts
{time 1}
{amount of time 1; period 3; period of time 1; time period 1}
|
Situations in which something (an instrument, substance, time, effort, force, money) is or can be used; e.g. to use, to spent, to represent, to mean, to be about, to operate, to fly, drive, run, eat, drink, consume. |
|
|
|
Usage stands for Situations in which either a resource or an instrument is used or activated for some purpose. This covers both consumptive usage (the use time, effort, food, fuel) and instrumental operation (as in to operate a vehicle, to run a program). So far it has been restricted to Dynamic Situations only. It typically combines with Purpose, Agentive and Cause because we often deliberately use things to cause to some effect for some purpose. |
Base Concepts
{unit 6; unit of measurement 1}
{consume 2; have 8; ingest 2; take 16}
|
An unobservable proposition which exists independently of time and space. They can be true or false rather than real. They can be asserted or denied, remembered or forgotten. E.g. idea, though, information, theory, plan. |
Base Concepts
{attitude 3; mental attitude 1}
{cognitive content 1; content 2; mental object 1}
{concept 1; conception 3}
{idea 2; thought 2}
{know-how 1; knowhow 1}
{message 2; content 3; subject matter 1; substance 4}
{method 2}M